UMBILICAL HERNIA & TREATMENT
If you have a soft bulge or lump near the navel that is visible especially when coughing or straining and is accompanied by mild pain, discomfort, or noticeable swelling, seek medical evaluation for the possibility of Umbilical Hernia.
What is Umbilical Hernia?
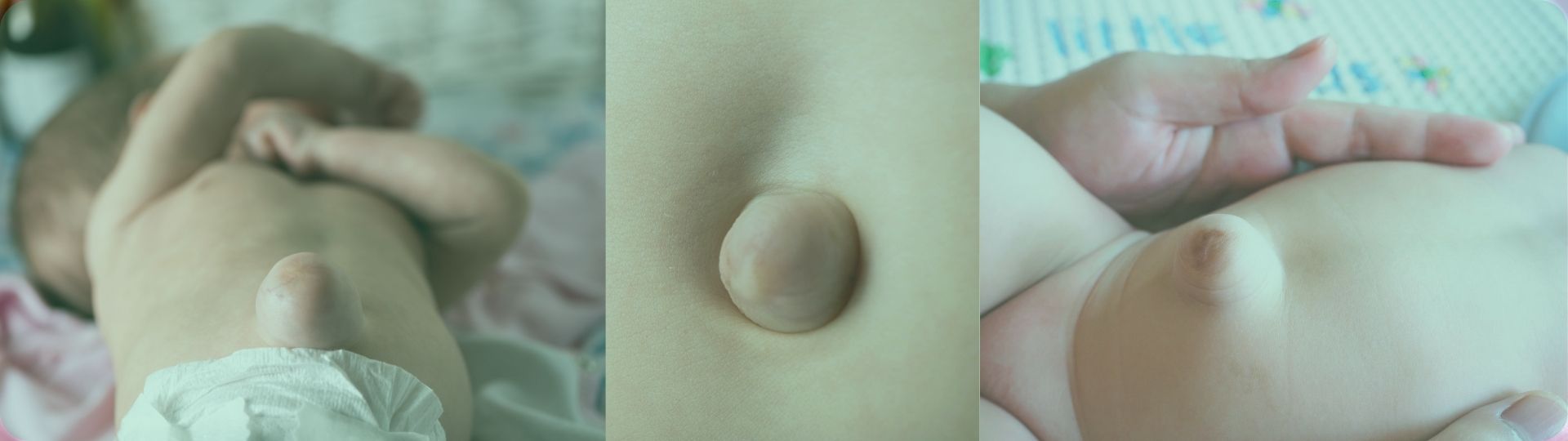
Visible as a small bulge around the navel, umbilical hernia is a condition where a portion of the intestine or abdominal tissue protrudes through an opening or weakness in the abdominal muscles near the navel (umbilicus). The bulge may be more prominent during episodes of coughing, cries or strenuous activities. Umbilical hernia is more common in children than in adults.
For doctors to classify a protrusion as an umbilical hernia, it must occur within 3 cm of the naval. This type of hernia is common in infants and typically resolves independently.
Umbilical Hernia Facts
Hernia in Children
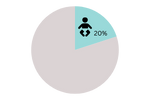
20% children are born with umbilical hernias
Umbilical hernias are more premature and low birth weight babies
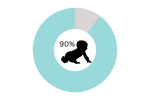
Over 90% of umbilical hernias close on their own by the age of 2
Hernia in Adults
Epigastric Hernias are often misdiagnosed as an umbilical hernia
Hernia in adults does not go away or get better without treatment

It is more common in females with a ratio of 3:1
Umbilical Hernia Causes
In Children
In children, hernias often occur due to a weakness or opening in the abdominal muscles, allowing abdominal contents to protrude. The causes of hernias in children include:

During foetal development, the abdominal wall may not fully close, leading to potential weak spots where a hernia can develop.

Premature infants may have underdeveloped abdominal muscles, increasing the risk of hernias.

There may be a genetic predisposition to hernias in some families.

Conditions that cause increased pressure in the abdominal cavity, such as persistent crying or constipation, can contribute to hernia formation.

Some children may have inherent weaknesses in the abdominal muscles, making them more susceptible to hernias.
In Adults
Umbilical hernias in adults typically occur when there is a weakness or opening in the muscles around the navel (umbilicus), allowing abdominal contents to protrude. The causes of umbilical hernias in adults include:

Excess body weight can place increased pressure on the abdominal muscles, leading to the development of hernias.

The stretching and weakening of the abdominal muscles during pregnancy can contribute to the formation of umbilical hernias.

Previous abdominal surgeries, especially if they involve incisions near the umbilical region, can weaken the abdominal muscles and increase the risk of hernias.

Accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity (ascites) can exert pressure on the abdominal wall, contributing to hernia formation.

Conditions that cause persistent coughing, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) or smoking, can strain the abdominal muscles and lead to hernias.

Women who have had multiple pregnancies may be at an increased risk due to repeated stretching of the abdominal muscles.

Regularly engaging in heavy lifting without proper abdominal support can strain the muscles and contribute to hernia development.

As individuals age, the abdominal muscles may naturally weaken, increasing the susceptibility to hernias.

Certain connective tissue disorders or collagen deficiencies can weaken the abdominal muscles and contribute to hernia formation.

Straining during bowel movements, often associated with chronic constipation, can contribute to the development of hernias.
It’s important to note that while these factors can increase the risk of umbilical hernias, not everyone with these risk factors will develop a hernia. If an individual notices symptoms such as a bulge near the navel, especially during activities that increase intra-abdominal pressure, it’s crucial to seek medical evaluation for a proper diagnosis and appropriate management.
Umbilical Hernia Symptoms
The symptoms of an umbilical hernia can vary in severity. Common signs and symptoms include:
Visible Bulge

Discomfort or Pain

Swelling

Redness or Discoloration

Vomiting or Nausea
It’s important to note that in many cases, umbilical hernias are asymptomatic, meaning they do not cause noticeable symptoms or discomfort. In infants, umbilical hernias are often harmless and tend to resolve on their own as the abdominal muscles strengthen.
However, if an adult experiences persistent pain, discomfort, or if the bulge becomes larger, it’s essential to seek medical attention. Complications such as incarceration (when the hernia contents become trapped) or strangulation (when blood flow to the hernia contents is compromised) are rare but serious and require immediate medical intervention.
If you suspect you have an umbilical hernia or are experiencing symptoms, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and guidance on appropriate management.
Umbilical Hernia Treatment
How to cure umbilical hernia in children?
In infants, umbilical hernias are often harmless and tend to close on their own as the abdominal muscles develop. Observation is typically recommended, and surgery is not usually required.
How to cure umbilical hernia in adults?
In adults, especially if the hernia is symptomatic, progressively increasing in size, or causing pain, surgical repair is commonly recommended. The surgery is known as herniorrhaphy or hernioplasty. You can read more about different treatments for hernia possible.
Making certain lifestyle changes, especially if obesity or heavy lifting contributed to the hernia, may be recommended to prevent recurrence.
An expert and experienced doctor is the best person to consult for everything related to Umbilical Hernia.
Dr.Sushil has been treating different types of Hernia for more than 15 years. He has patients from across the country and even abroad. Read more about him.